Simplicial Complex in Two Dimensions
A brief summary.
edge: asecond orderingedge(:,1)<edge(:,2);locEdge: the default one is the consistent orientation which will be counter-clockwise ifelemis positive ordered. The asecond orientation is used for edge elements.- consistent orientation
[2 3; 3 1; 1 2]; - asecond orientation
[2 3; 1 3; 1 2];
- consistent orientation
elem: the default one is positive ordering and the asecond ordering is used for edge elements.- Use
[elem,bdFlag] = sortelem(elem,bdFlag)to change to the ascend ordering. Note thatbdFlagshould be switched together. - Use
[elem,idx,area,bdFlag] = fixorder(node,elem,bdFlag)to change the ordering to the positive ordering.
The multigrid solvers use the original ordering of
elemobtained from either uniform refinement or bisection methods. So letelemold=elemand useelemoldin multigrid solvers.
- Examples on the usage:
PoissonRT0, PoissonBDM1
Outline
We describe the data structure of the simplicial complex associated to a
two-dimensional triangulation give by node,elem. The node records
the coordinates of vertices and elem is the pointer from the local to
the global indices of vertices. See Basic mesh data structure.
node = [0,0; 1,0; 1,1; 0,1]; % nodes
elem = [2,3,1; 4,1,3]; % elements
N = size(node,1); NT = size(elem,1); % NE = size(edge,1);
showmesh(node,elem);
findelem(node,elem);
findnode(node);
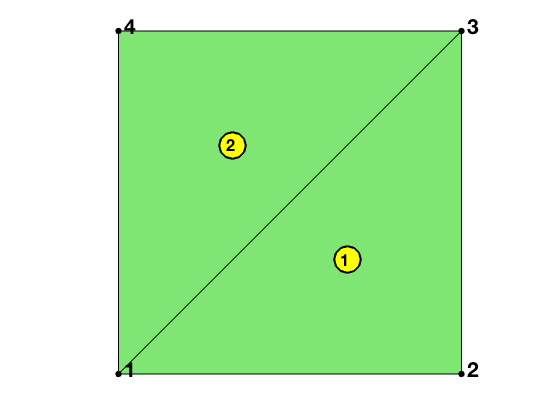
The integers N, NE, NT represents the muber of vertice, edges, triangles
respectively.
The corresponding simplicial complex consists of vertices, edges and triangles. We shall discuss the following three issues:
- Indexing of simplexes
- Ordering of vertices of simplexes
- Orientatoin of simplexes
The indexing and ordering are related and the ordering and orientation
are mixed together. However the indexing has nothing to do with the
orientation. The indexing and ordering are the combinarotry structure,
i.e. only elem is needed, while the orientation also depends on node,
the geometry emembdding of vertices.
For indexing, ordering and orientation, there are always two versions: local and global. The pointer from the local and the global version is the most complicated issue.
Indexing
The indexing refers to the numbering of simplexes, e.g., which edge is
numbered as the first one. Each simplex in the simplicial complex has a unique index which is called the global index. Inside one triangle, the three vertices and three
edges have their local index 1:3.
In the assembling procedure of finite element methods, an element-wise
matrix using the local index is firstly computed and then assembled to get a
big matrix using the global index. Thus the pointer from the local
index to the global one is indispensible. For bases independent of
the ordering and orientation, e.g., P1 and P2 elements, the pointer of indices
is sufficient.
Pointers of vertices
The NT x 3 matrix elem is indeed the pointer of the vertex indices. For example elem(t,1)=25 means the first vertex of t is the 25-th vertex.
Similiary, the NE x 2 matrix edge records the vertices pointer of edges.
Local indexing of edges
The triangle constists of three vertices indexed as [1,2,3] and contains three edges. Consider two local indexing schemes for those edges:
- Opposite indexing
locEdge = [2,3; 3,1; 1,2]
In locEdge, the i-th edge is opposite to the i-th verices and thus
called opposite indexing.
- Lexicogrphic indexing
locEdgel = [1,2; 1,3; 2,3]
In locEdgel, the indexing is induced from the lexicographic ordering of indices of the three edges.
Note that the ordering of vertices inside one edge will not change the indexing. For example, locEdge = [2,3; 1,3; 1,2] use the same opposite indexing but different ordering. For the 2nd edge, choosing [1 3] or [3 1] depends on the consideration of orientation and ordering.
For 2-D triangulations, we shall always chose opposite indexing. The lexicographic indexing is mainly used in the construction of face2edge of 3-D triangulations; see Simplicial Complex in Three Dimensions.
Global indexing of edges
One can easily collect all edges elementwise. The issue is the duplication. For example, each interior edge will be counted twice. The unique funciton can be applied such that each edge has a unique global index.
totalEdge = uint32([elem(:,[2,3]); elem(:,[3,1]); elem(:,[1,2])]);
sortedTotalEdge = sort(totalEdge,2);
[edge,tempvar,je] = unique(sortedTotalEdge,'rows');
Pointers of edges
elem2edge(1:NT,1:3) records the pointer from the local to the global index of edges. For example, elem2edge(t,1) = 10 means the first edge of triangle t (which is formed by [2 3] vertices of t) is the 10-th one in the edge array.
Such information is stored in the third output of unique function and can be reshaped to the desired size:
elem2edge = uint32(reshape(je,NT,3));
Note that the pointer elem2edge depends on the local indexing of edges
used in the generation of totalEdge. Here the opposite indexing of
three local edges is used.
Ordering
We discuss the ordering of vertices of simplexes. The local and the global ordering may not be consistent and a sign array can be used to record the inconsistency.
The local ordering refers to the ordering of local veritces. It will be used in the formulation of the local basis and thus the ordering does matter.
The global ordering refers to the ordering of the global index of vertices.
elem
The local ordering is always [1,2,3]. Any permutation of three veritces of a triangle still represents the same triangle. Such freedom provide a room to record more information like: an global ordering of vertices, an orientation of triangles, and refinement rules
Two types of ordering is of particular importance
- positive ordering
- ascend ordering
In the positive ordering, the three vertices are ordered such that the
signed area, det(v12,v13), is positive. If elem is not positive
ordered, elem = fixorder(node,elem) will compute the signed area and switch the vertices for triangles with negative areas.
For 2-D triangulations, three vertices of a triangle in 2-D is sorted counter-clockwise and the first vertex is chosen as the newest vertex. Such ordering enables the efficient implementation of the bisection refinement and coarsening in 2-D; see Bisection in Two Dimensions and Coarsening in Two Dimensions. Positive ordering is the default choice and used in most places.
In the ascend ordering, the vertices of elem is sorted ascendly according to the global index of indices, i.e.
elem(t,1) < elem(t,2) < elem(t,3)
This can be easily achieved by elem = sort(elem,2). However, one has to rotate the boundary flag accordingly using sortelem.
bdFlag = setboundary(node,elem,'Dirichlet');
display('Before rotation'); display(elem); display(bdFlag);
[elem,bdFlag] = sortelem(elem,bdFlag);
display('After rotation'); display(elem); display(bdFlag);
Before rotation
elem =
2 3 1
4 1 3
bdFlag =
0 1 1
0 1 1
After rotation
elem =
1 2 3
1 3 4
bdFlag =
1 0 1
1 1 0
Ascend ordering will benefit the construction of local bases for high order Lagrange elements and in general bases with orientation dependent.
We may switch the default positive ordering of elem to the ascend ordering
when generating data structure for finite element basis. However such
sorting is always hidden inside the subroutines; see PoissonRT0 and PoissonBDM1.
edge
The global ordering of edges is always ascended, i.e.
edge(:,1) < edge(:,2);
Indeed in the generation of edge, the totalEdge is sorted to the
ascend ordering so that unique can be applied to eliminate the duplication.
Recall that we always use the opposite indexing of edges in two dimensions. With the same indexing, we may use
- ascend ordering
[2 3; 1 3; 1 2]; - (orientation) consistent ordering
[2 3; 3 1; 1 2];
It is consistent since the local ordering orientation of edges is consistent with the induced orientation as the boundary of a triangle; see the discussion on the orientation.
Even for the orientation consistent ordering, there might be an inconsistency between the local and global ordering. Namely edge(elem2edge(t,1),1) > edge(elem2edge(t,1),2) may happen.
Orientation
The orientation of a triangle is the sign of the signed area. The orientation of an edge is given by a tangential or a normal vector, which is obtained by rotate a given tangential vector by 90 degree clockwise. When edges are counter-clockwise orientated, the corresponding normal vector is the outwards normal vector.
The orientation of a d-simplex will induce an orientation of its d-1 subcomplex on the boundary and is called the induced orientation. For example, a positive orientated triangle will induce the counter-clockwise orientation of its three edges.
The ordering of vertices will naturally introduce an orientation and will be called the ordering-orientation. More specifically
- The vector from
edge(:,1)toedge(:,2)defines an orientation of edges. - The sign of
det(v12,v13)defines an orientation of triangles.
The orientation of a simplex in the simplicial complex should be uniquely determined which will be called the global orientation. It can be chosen as the global ordering-orientation but not always the case.
Inside one triangle, the local orientation of three edges is more involved. The local ordering of edges will introduce a local ordering orientation. The orientation of the triangle will also induce an induced orientation. The local ordering-orientation is used in the computation of local bases and the induced orientation is used when computing the differential operator locally. They may or may not be consistent with the global orientation of edges.
In general, there will be an inconsistency of the following types of orientation of simplexes and appropriate data structure should be constructed to record such inconsistency.
- a global orientation
- the global ordering-orientation
- the local ordering-orientation
- the local induced orientation
elem
The orientation of a triangle is either positive or negative. For
the global ordering-orientation, it is the sign of the signed area
(output of simplexvolume).
[Dlambda,area,elemSign] = gradbasis(node,elem);
In the output of gradbasis, area is always positive and an additional
array elemSign is used to record the sign of the signed area.
Dlambda(t,:,k) is the gradient of the barycentric coordinate $\lambda_k$ associated to vertex $k$. Therefore the outward normal direction of the kth edge can be obtained by -Dlambda(t,:,k) which is independent of the orientation of triangle t.
edge
For 2-D triangulations, we shall always chose the global ascend ordering orientation, i.e., from the smaller index to the bigger index.
The local ordering-orientation is implicitly used when computing finite
element basis in each element. For example, the edge element on edge [i j]
in locEdge is defined as
Permutation of [i j] to [j i] will change the sign of the basis. Note
that this is locally, i.e., element by element.
The global basis associated to this edge, however, depends only on its
global orientation. The array elem2edgeSign(1:NT, 1:3) records the inconsistency of a local ordering-orientation and the global orientation.
For the consistent local ordering [2 3; 3 1; 1 2] and the global ascend
ordering-orientation, the elem2edgeSign can be generated as follows:
elem2edgeSign = ones(NT,3,'int8');
totalEdge = uint32([elem(:,[2,3]); elem(:,[3,1]); elem(:,[1,2])]);
idx = (totalEdge(:,1)>totalEdge(:,2));
elem2edgeSign(idx) = -1;
There is one more inconsistency between the induced orientation and the global orientation of edges. If a triangle is positive orientated, the induced edge orientation should be given by the outwards (relative to a triangle) normal vector. This induced orientation may not be consistent with the global orientation of edges.
It depends on the ordering of elem and locEdge. When elem is
positive ordered and locEdge is consistently ordered, it is.
In the ascend ordering of elem and edge, we denote the direction as +1
if the direction of an edge is the same with the induced direction in a
certain elem, and -1 otherwise. Then the consistency is given by
elem2edgeSign = [+1 -1 +1];
The second sign is -1 because the local edge in the ascend ordering is [1
3] not [3 1].
The elem2edgeSign will be used when assembling differential operators.
For example, when computing div operators on a positive orientated
triangle, the edge should have outwards normal direction or equivalently
the counter-clockwise orientation.
Summary
We summarize the two popular ordering and orientation schemes below.
Positive Ordering and Orientation
The vertices of the elem are sorted such that the area is always positive. i.e. the three vertices of the elem are ordered counter-clockwisely. Furthermore the first vertex is always the newest vertex of the triangle for the easy of the adaptive mesh refinement (bisection) and coarsening.
The local edge is using the opposite indexing and the consistent ordering
locEdge = [2,3; 3,1; 1,2]
The ascend ordering is used for the global edges, i.e., edge is ascend sorted
edge(:,1) < edge(:,2)
The inconsistency of the orientation is recorded in elem2edgeSign by
totalEdge = uint32([elem(:,[2,3]); elem(:,[3,1]); elem(:,[1,2])]);
idx = (totalEdge(:,1)>totalEdge(:,2));
elem2edgeSign(idx) = -1;
This is the default ordering and orientation scheme.
Ascend Ordering and Orientation
For H(curl) and H(div) elements and high order (cubic and above) Lagrange elements, we will use the ascend ordering and orientation.
Ordering. The vertices of elem are sorted such that
elem(t,1)<elem(t,2)<elem(t,3)
The ascend ordering is used for edges
edge(:,1) < edge(:,2)
The local edge is also in the ascend ordering
locEdge = [2,3; 1,3; 1,2]
The benefit of the ascend ordering: the ordering of local edges is consistent with the global ones and so is the corresponding orientation. So there is no need to use elem2edgeSign for the assembling of mass matrices.
Orientation. We choose the ordering-orientation.
elem:sign(det(v12,v13))edge: from the node with the smaller global index to the bigger one
The induced orientation inside one triangle may not be consistent with the ordering-orientation. Such inconsistency is recorded in
elem2edgeSign = [+1 -1 +1]
and will be used when computing the different operator by the incidence matrix, i.e., div operator.
Example
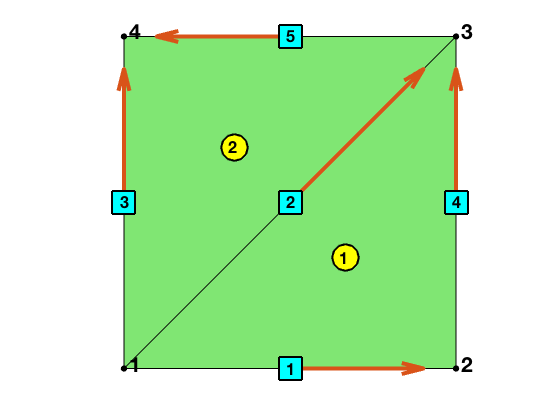
node = [0,0; 1,0; 1,1; 0,1]; % nodes
elem = [2,3,1; 4,1,3]; % elements
%% Poistive ordering and orientation
[elem2edge,edge,elem2edgeSign] = dofedge(elem);
showmesh(node,elem);
findnode(node);
findelem(node,elem);
findedge(node,edge,'all','vec');
%%
display(elem);
display(edge);
display(elem2edge);
display(elem2edgeSign);
elem =
2 3 1
4 1 3
edge =
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
3 4
elem2edge =
2 1 4
2 5 3
elem2edgeSign =
-1 1 1
1 1 -1
node = [0,0; 1,0; 1,1; 0,1]; % nodes
elem = [2,3,1; 4,1,3]; % elements
%% Ascend Ordering and Orientation
bdFlag = setboundary(node,elem,'Dirichlet');
[elem,bdFlag] = sortelem(elem,bdFlag);
[elem2edge,edge,elem2edgeSign] = dofedge(elem);
showmesh(node,elem);
findnode(node);
findelem(node,elem);
findedge(node,edge,'all','vec');
display(elem);
display(edge);
display(elem2edge);
display(elem2edgeSign);
elem =
1 2 3
1 3 4
edge =
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
3 4
elem2edge =
4 2 1
5 3 2
elem2edgeSign =
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
Comments