Weak Galerkin Methods for Poisson Equation in 3D
This example is to show the rate of convergence of the linear finite element approximation of the Poisson equation on the unit cube:
\[- \Delta u = f \; \hbox{in } (0,1)^3\]for the following boundary conditions
- Non-empty Dirichlet boundary condition: $u=g_D \hbox{ on }\Gamma_D, \nabla u\cdot n=g_N \hbox{ on }\Gamma_N.$
- Pure Neumann boundary condition: $\nabla u\cdot n=g_N \hbox{ on } \partial \Omega$.
- Robin boundary condition: $g_R u + \nabla u\cdot n=g_N \hbox{ on }\partial \Omega$.
References:
- Quick Introduction to Finite Element Methods
- Introduction to Finite Element Methods
- Progamming of Finite Element Methods
Subroutines:
- Poisson3WG
- cubePoisson3WG
- femPoisson3
- Poisson3WGfemrate
The method is implemented in Poisson3 subroutine and tested in cubePoisson. Together with other elements (P1, P2,Q1,WG), femPoisson3 provides a concise interface to solve Poisson equation. The P1 element is tested in Poisson3femrate. This doc is based on Poisson3femrate.
The Lowest Order Weak Galerkin Element
The basis and the local matrices can be found in Progamming of Weak Galerkin Methods
Mixed boundary condition
%% Setting
[node,elem] = cubemesh([0,1,0,1,0,1],0.5);
mesh = struct('node',node,'elem',elem);
option.L0 = 1;
option.maxIt = 4;
option.elemType = 'WG';
option.printlevel = 1;
option.plotflag = 1;
%% Non-empty Dirichlet boundary condition.
pde = sincosdata3;
mesh.bdFlag = setboundary3(node,elem,'Dirichlet','~(x==0)','Neumann','x==0');
femPoisson3(mesh,pde,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 6528, #nnz: 25576, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 7.80e-09, time = 0.14 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 50688, #nnz: 223244, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 9.10e-09, time = 0.28 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 399360, #nnz: 1815764, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 9.78e-09, time = 2.6 s
Table: Error
#Dof h ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
864 2.500e-01 1.62586e-02 5.82293e-01 2.08771e-01 2.74409e-02
6528 1.250e-01 4.03120e-03 2.94275e-01 9.83063e-02 7.18140e-03
50688 6.250e-02 1.00634e-03 1.47521e-01 4.83526e-02 1.81988e-03
399360 3.125e-02 2.51527e-04 7.38079e-02 2.40757e-02 4.58839e-04
Table: CPU time
#Dof Assemble Solve Error Mesh
864 1.70e-01 9.68e-03 9.00e-02 1.00e-02
6528 1.10e-01 1.39e-01 4.00e-02 2.00e-02
50688 4.10e-01 2.82e-01 2.00e-01 9.00e-02
399360 4.14e+00 2.59e+00 1.77e+00 0.00e+00
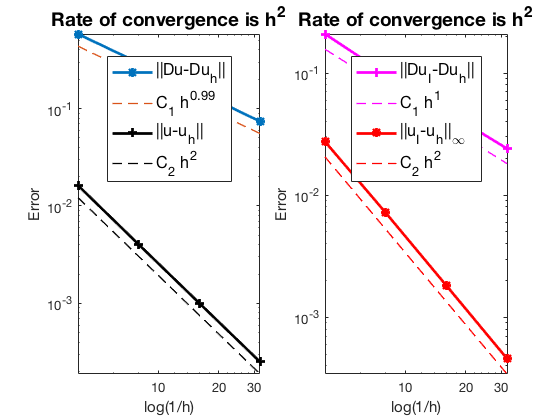
Pure Neumann boundary condition
When pure Neumann boundary condition is posed, i.e., $-\Delta u =f$ in $\Omega$ and $\nabla u\cdot n=g_N$ on $\partial \Omega$, the data should be consisitent in the sense that $\int_{\Omega} f \, dx + \int_{\partial \Omega} g \, ds = 0$. The solution is unique up to a constant. A post-process is applied such that the constraint $\int_{\Omega}u_h dx = 0$ is imposed.
%% Pure Neumann boundary condition.
option.plotflag = 0;
mesh.bdFlag = setboundary3(node,elem,'Neumann');
femPoisson3(mesh,pde,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 6528, #nnz: 27909, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 20, err = 7.29e-09, time = 0.1 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 50688, #nnz: 232473, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 21, err = 4.09e-09, time = 0.33 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 399360, #nnz: 1858773, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 22, err = 4.23e-09, time = 3.2 s
Table: Error
#Dof h ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
864 2.500e-01 2.14311e-02 5.83747e-01 2.58148e-01 1.21000e-01
6528 1.250e-01 5.28526e-03 2.94315e-01 1.08333e-01 3.88004e-02
50688 6.250e-02 1.31642e-03 1.47495e-01 4.97809e-02 1.03134e-02
399360 3.125e-02 3.28925e-04 7.38022e-02 2.42593e-02 2.61798e-03
Table: CPU time
#Dof Assemble Solve Error Mesh
864 6.00e-02 2.09e-03 2.00e-02 0.00e+00
6528 3.00e-02 1.01e-01 3.00e-02 1.00e-02
50688 3.90e-01 3.27e-01 1.60e-01 8.00e-02
399360 4.20e+00 3.25e+00 1.62e+00 0.00e+00
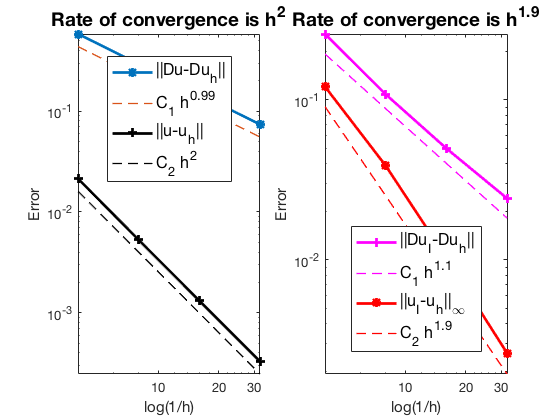
Robin boundary condition
%% Pure Robin boundary condition.
pde = sincosRobindata3;
mesh.bdFlag = setboundary3(node,elem,'Robin');
femPoisson3(mesh,pde,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 6528, #nnz: 27912, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 3.75e-09, time = 0.085 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 50688, #nnz: 232476, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 7.36e-09, time = 0.26 s
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method
#dof: 399360, #nnz: 1858776, smoothing: (1,1), iter: 17, err = 7.33e-09, time = 2.1 s
Table: Error
#Dof h ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
864 2.500e-01 2.06220e-02 5.78283e-01 2.29477e-01 5.01643e-02
6528 1.250e-01 5.16104e-03 2.93750e-01 1.01338e-01 1.36257e-02
50688 6.250e-02 1.29034e-03 1.47454e-01 4.87501e-02 3.60385e-03
399360 3.125e-02 3.22587e-04 7.37995e-02 2.41260e-02 9.11692e-04
Table: CPU time
#Dof Assemble Solve Error Mesh
864 4.00e-02 1.77e-03 1.00e-02 0.00e+00
6528 6.00e-02 8.46e-02 3.00e-02 1.00e-02
50688 3.00e-01 2.61e-01 1.80e-01 1.20e-01
399360 3.01e+00 2.15e+00 1.72e+00 0.00e+00
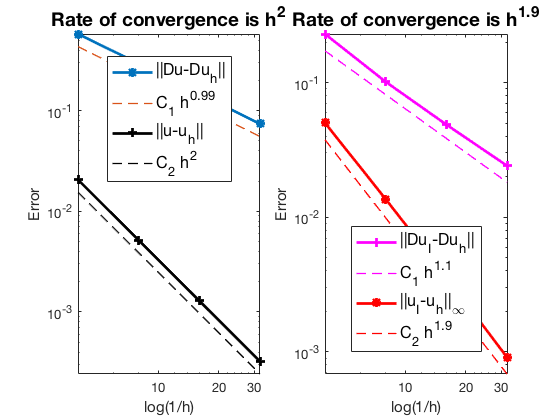
Conclusion
The optimal rate of convergence of the H1-norm (1st order) and L2-norm (2nd order) is observed. No superconvergence for $|\nabla u_I - \nabla u_h|$.
MGCG converges uniformly in all cases.
Comments