Lowest Order Edge Element for Maxwell Equations in 3D
This example is to show the lowest order edge element approximation of the electric field of the time harmonic Maxwell equation.
\[\begin{aligned} \nabla \times (\mu^{-1}\nabla \times u) - \omega^2 \varepsilon \, u &= J \quad \text{ in } \quad \Omega, \\ n \times u &= n \times g_D \quad \text{ on } \quad \Gamma_D, \\ n \times (\mu^{-1}\nabla \times u) &= n \times g_N \quad \text{ on } \quad \Gamma_N. \end{aligned}\]based on the weak formulation
\[(\mu^{-1}\nabla \times u, \nabla \times v) - (\omega^2\varepsilon u,v) = (J,v) - \langle n \times g_N,v \rangle_{\Gamma_N}.\]Reference
- Finite Element Methods for Maxwell Equations
- Programming of Finite Element Methods for Maxwell Equations
Subroutines:
- Maxwell
- cubeMaxwell
- femMaxwell3
- Maxwellfemrate
The method is implemented in Maxwell subroutine and tested in cubeMaxwell. Together with other elements (ND0,ND1,ND2), femMaxwell3 provides a concise interface to solve Maxwell equation. The ND0 element is tested in Maxwellfemrate. This doc is based on Maxwellfemrate.
Data Structure
Use the function
[elem2dof,edge,elem2edgeSign] = dof3edge(elem);
to construct the pointer from element index to edge index. Read Dof on Edges in Three Dimensions for details.
node = [1,0,0; 0,1,0; 0,0,0; 0,0,1];
elem = [1 2 3 4];
localEdge = [1 2; 1 3; 1 4; 2 3; 2 4; 3 4];
set(gcf,'Units','normal');
set(gcf,'Position',[0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25]);
showmesh3(node,elem);
view(-72,9);
findnode3(node);
findedge(node,localEdge,'all','vec');
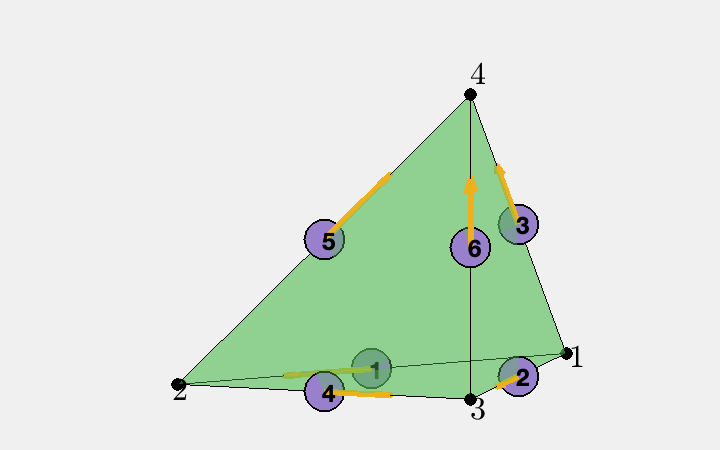
The six dofs associated to edges in a tetrahedron is sorted in the ordering [1 2; 1 3; 1 4; 2 3; 2 4; 3 4]. Here [1 2 3 4] are local indices of vertices.
Globally we use ascend ordering for each element and thus the orientation of the edge is consistent. No need of elem2edgeSign. Read Simplicial complex in three dimensions for more discussion of indexing, ordering and orientation.
Local Bases
Suppose [i,j] is the kth edge and i<j. The basis is given by
Inside one tetrahedron, the 6 bases functions along with their curl
corresponding to 6 local edges [1 2; 1 3; 1 4; 2 3; 2 4; 3 4] are
Degree of freedoms
Suppose [i,j] is the kth edge and i<j. The corresponding degree of freedom is
It is dual to the basis ${\phi_k}$ in the sense that
\[l_{\ell}(\phi _k) = \delta_{k,\ell}.\]Dirichlet boundary condition
%% Setting
[node,elem] = cubemesh([-1,1,-1,1,-1,1],1);
mesh = struct('node',node,'elem',elem);
option.L0 = 1;
option.maxIt = 4;
option.elemType = 'ND0';
option.printlevel = 1;
%% Dirichlet boundary condition.
fprintf('Dirichlet boundary conditions. \n');
pde = Maxwelldata2;
bdFlag = setboundary3(node,elem,'Dirichlet');
femMaxwell3(mesh,pde,option);
Dirichlet boundary conditions.
#dof: 604, Direct solver 0
#dof: 4184, Direct solver 0.03
Conjugate Gradient Method using HX preconditioner
#dof: 31024, #nnz: 411904, iter: 26, err = 7.0419e-09, time = 0.54 s
Conjugate Gradient Method using HX preconditioner
#dof: 238688, #nnz: 3525680, iter: 29, err = 5.6720e-09, time = 3.5 s
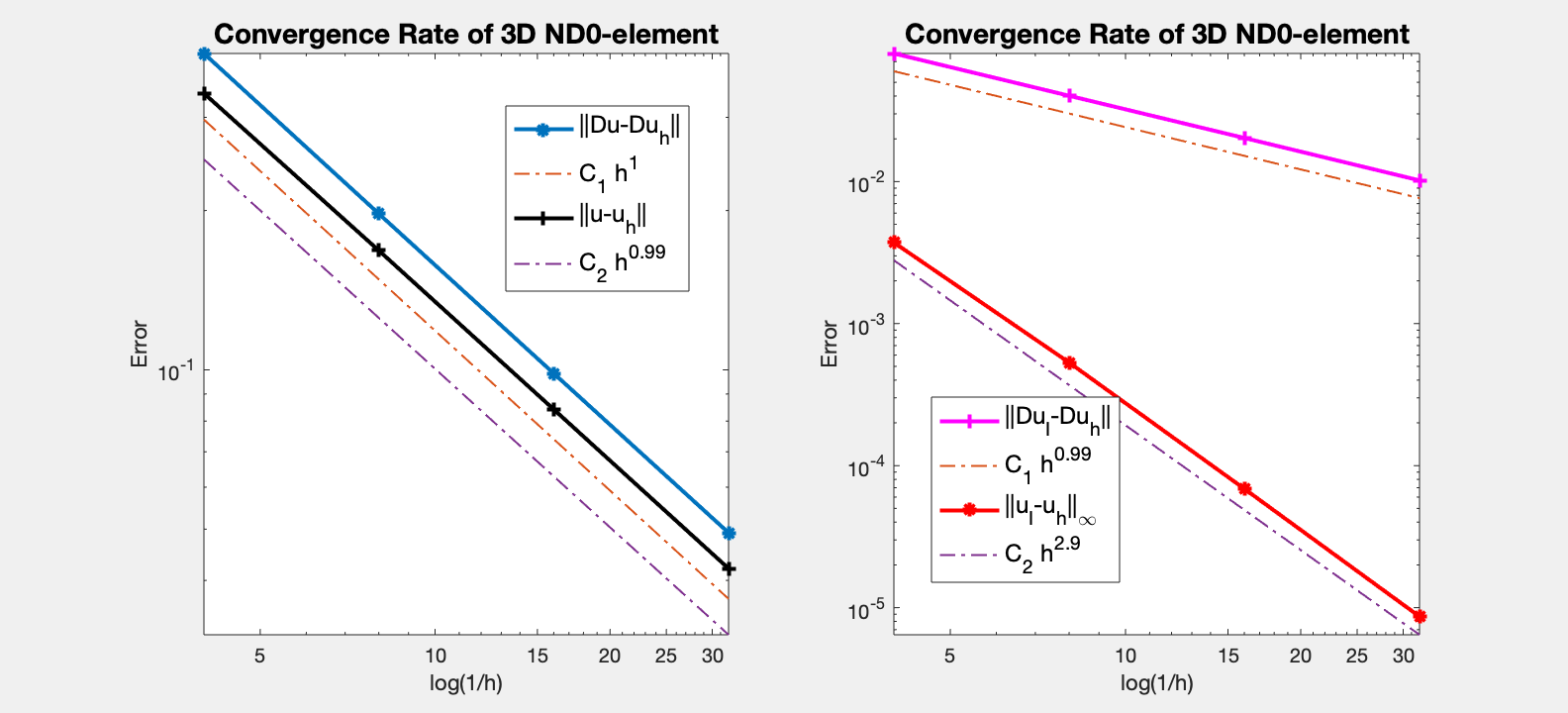
Table: Error
#Dof h ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
604 2.500e-01 3.33015e-01 3.96024e-01 7.98367e-02 3.72532e-03
4184 1.250e-01 1.68028e-01 1.97196e-01 4.02280e-02 5.32169e-04
31024 6.250e-02 8.42042e-02 9.84691e-02 2.02873e-02 6.87268e-05
238688 3.125e-02 4.21257e-02 4.92119e-02 1.01979e-02 8.65951e-06
Table: CPU time
#Dof Assemble Solve Error Mesh
604 2.00e-02 0.00e+00 2.00e-02 0.00e+00
4184 5.00e-02 3.00e-02 7.00e-02 1.00e-02
31024 3.60e-01 5.40e-01 3.00e-01 5.00e-02
238688 2.95e+00 3.48e+00 2.23e+00 0.00e+00
Pure Neumann boundary condition
fprintf('Neumann boundary condition. \n');
option.plotflag = 0;
pde = Maxwelldata2;
mesh.bdFlag = setboundary3(node,elem,'Neumann');
femMaxwell3(mesh,pde,option);
Neumann boundary condition.
#dof: 604, Direct solver 0.01
#dof: 4184, Direct solver 0.04
Conjugate Gradient Method using HX preconditioner
#dof: 31024, #nnz: 482608, iter: 18, err = 5.5383e-09, time = 0.41 s
Conjugate Gradient Method using HX preconditioner
#dof: 238688, #nnz: 3814496, iter: 19, err = 4.7105e-09, time = 2.6 s
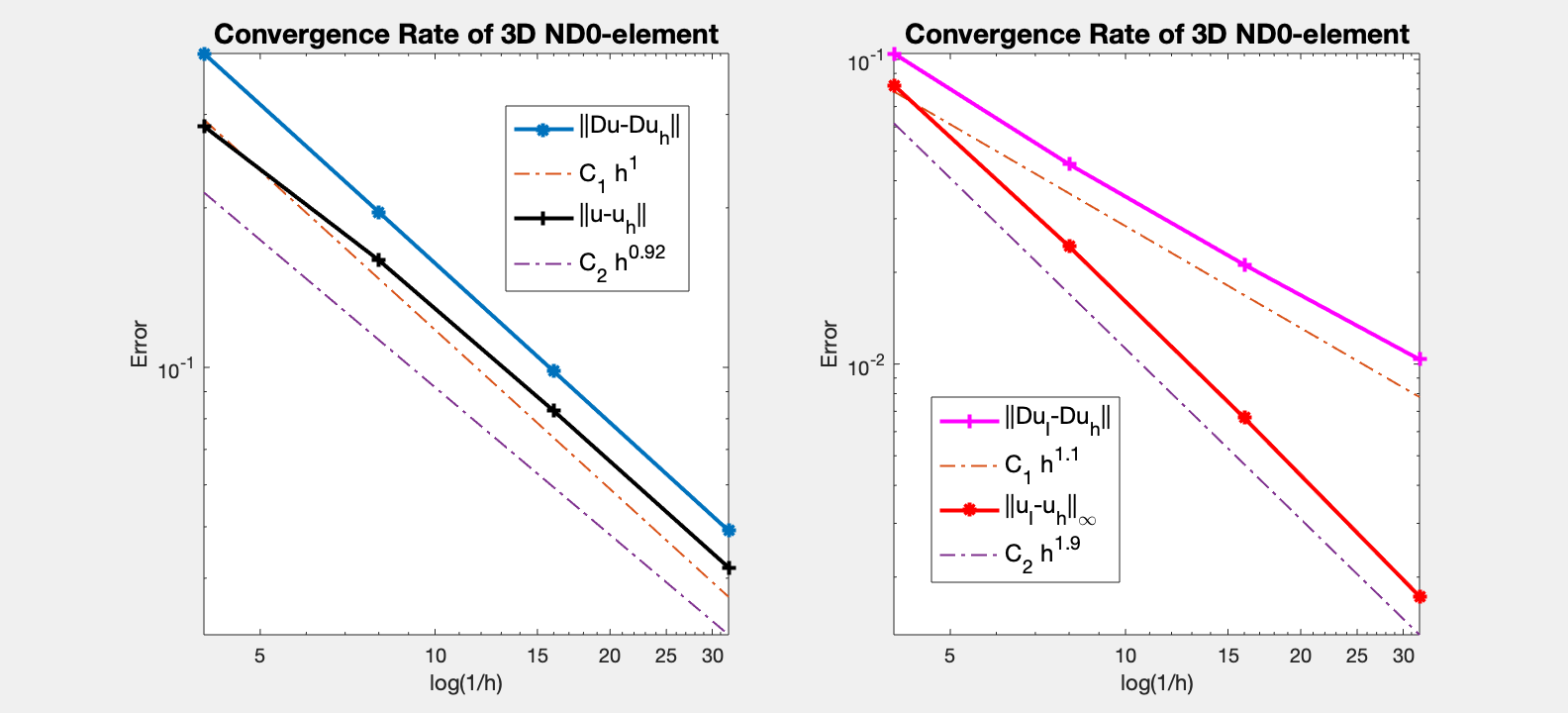
Table: Error
#Dof h ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
604 2.500e-01 2.85095e-01 3.91208e-01 1.04607e-01 8.22886e-02
4184 1.250e-01 1.59317e-01 1.96376e-01 4.52796e-02 2.43444e-02
31024 6.250e-02 8.27814e-02 9.83230e-02 2.11913e-02 6.66042e-03
238688 3.125e-02 4.19067e-02 4.91846e-02 1.03572e-02 1.72821e-03
Table: CPU time
#Dof Assemble Solve Error Mesh
604 3.00e-02 1.00e-02 3.00e-02 0.00e+00
4184 8.00e-02 4.00e-02 7.00e-02 0.00e+00
31024 3.60e-01 4.10e-01 2.90e-01 5.00e-02
238688 2.86e+00 2.58e+00 2.20e+00 0.00e+00
Conclusion
The optimal rate of convergence of both the H(curl)-norm and L2-norm (1st order) is observed. The 2nd order convergent rate between two discrete functions $| \nabla \times (u_I - u_h) |_{\infty}$ is known as superconvergence.
MGCG using HX preconditioner converges uniformly in all cases.
Comments